The Las Piedras River, a major tributary of the Madre de Dios River in the southeast of the Peruvian Amazon, is increasingly being recognized for its exceptional wildlife, and by presence of indigenous peoples in voluntary isolation.
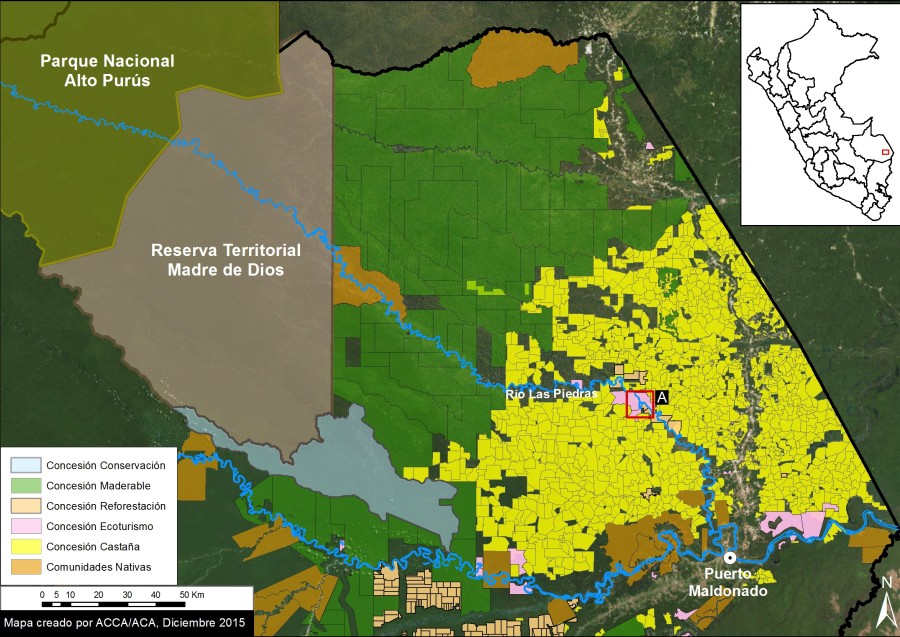
The Las Piedras River in the southern Peruvian Amazon (department of Madre de Dios) is increasingly recognized for its outstanding wildlife (for example, see this video by naturalist and explorer Paul Rosolie, and this trailer for the upcoming film Uncharted Amazon). As seen in Image 23a, its headwaters are born in the Alto Purus National Park, but the lower Las Piedras is surrounded by a mix of different types of forestry concessions (logging, Brazil nut harvesting, ecotourism, and reforestation).
Here in MAAP #23, we document the growing deforestation on the lower Las Piedras River in the area surrounding the community of Lucerna (see red box in Image 23a for context).

Image 23a. Las Piedras River and surrounding designations. Data: MINAGRI, IBC, SERNANP.
Deforestation Analysis
Image 23b shows our deforestation analysis for an area along the lower Las Piedras River near the community of Lucerna (see red box in Image 23a for context). We found a sharp increase in deforestation starting in 2012. In the 11 years between 2000 and 2011, we detected the deforestation of 88 hectares (218 acres). In contrast, in the 4 years between 2012 and 2015, we detected the deforestation of 472 hectares (1,166 acres). 2015 had the highest deforestation total with 155 hectares (383 acres).

Image 23b. Lower Las Piedras River deforestation analysis. Data: MINAGRI, PNCB/MINAM, Hansen/UMD/Google/USGS/NASA.
Note that the Las Piedras Amazon Center (LPAC) Ecotourism Concession represents an effective barrier to deforestation. However, note that two other, less active, ecotourism concessions are experiencing extensive deforestation. The 4,460 hectare LPAC concession (which was created in 2007 and transferred to ARCAmazon in March 2015) hosts an active tourist lodge, research center, and Forest Ranger Protection Program, which employs local people to patrol the area while monitoring wildlife and human impacts.

Image 23c. Recent Landsat image showing deforestation along lower Las Piedras. Data: USGS,MINAGRI.
Image 23c shows a very recent (December 2015) Landsat image of the deforestation highlighted in Image 23b. The pinkish-red areas indicate the most recently cleared forests. We have received information indicating that much of this new deforestation is associated with cacao plantations. Cacao is of course used to produce chocolate.
– This report was originally published in MAAP and is republished by an agreement to share content.